This article applies as of PRTG 22
Instructions on how to set up Sigfox callbacks and configure the HTTP IoT Push Data Advanced sensor in PRTG to monitor Sigfox Geolocation data.
Monitoring Sigfox geolocation with PRTG
Sigfox Geolocation is a low-energy location service for devices that are equipped with a Sigfox module, without the need for GPS. For each message sent by a device, Sigfox Geolocation provides real-time coordinates and the location within a few hundred meters up to a kilometer, delivered through a callback, for example.
With PRTG, you can monitor Sigfox devices with the HTTP IoT Push Data Advanced sensor.
Create an HTTP IoT Push Data Advanced sensor
The first step to monitoring Sigfox Geolocation is to add an HTTP IoT Push Data Advanced sensor to your PRTG installation.
- Create a new device or use an existing device and enter 127.0.0.1 as the IPv4 Address/DNS Name.
- Add an HTTP IoT Push Data Advanced sensor to the device.
- Note the TLS Port 5051 and the Identification Token, you need both values when setting up your Sigfox callback configuration, so copy them.
Create a Sigfox callback
The next step to monitoring Sigfox Geolocation is to create the corresponding callback in the Sigfox interface.
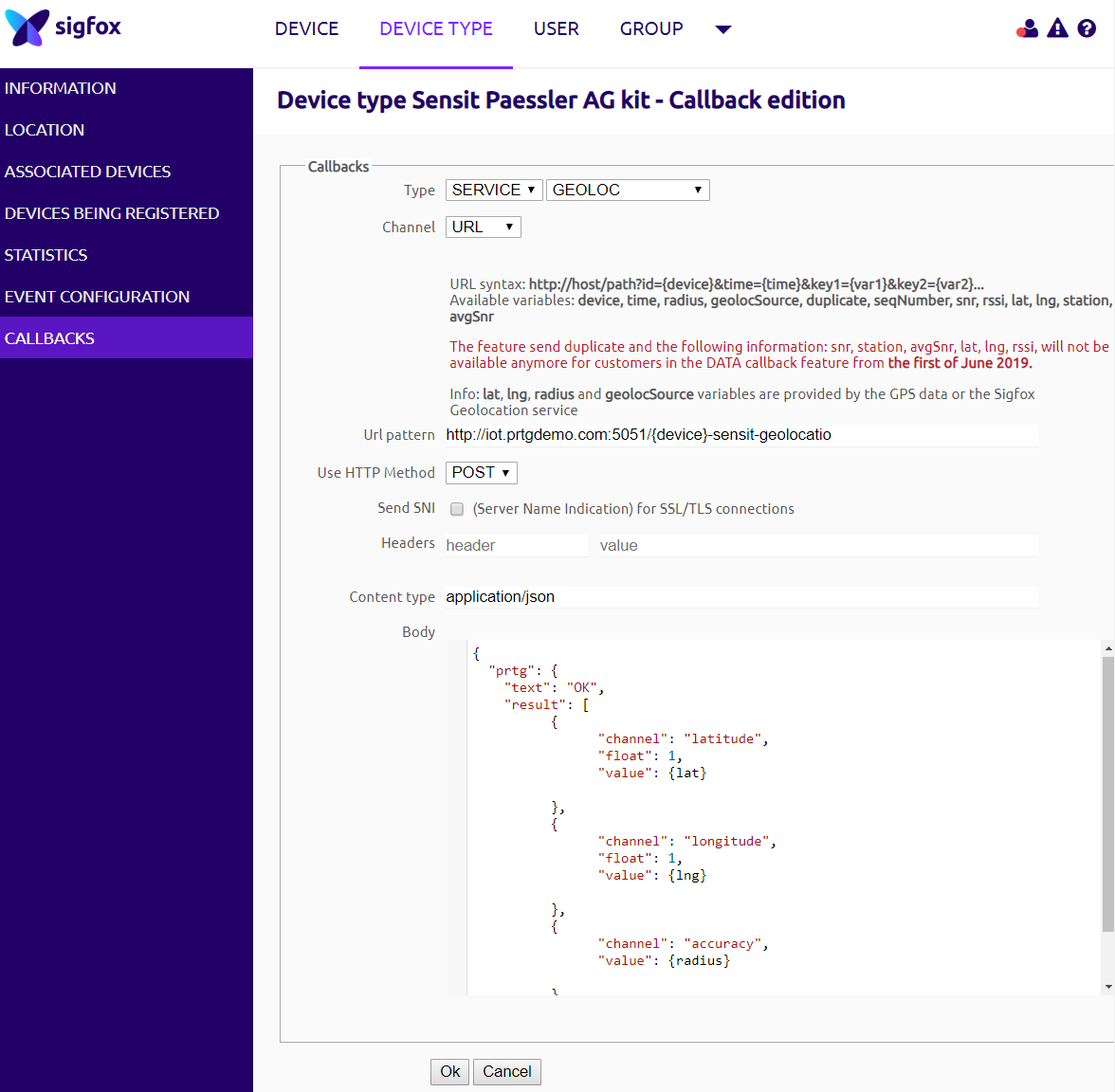
- Open Callbacks.
- Select the Device Type tab.
- Under Type, select Service and Geoloc.
- Under Channel, select URLand enter the following URL.
Note: You can reference the Sigfox Id as {device} in your <token>.https://<probe_IP>:5051/<token> - Replace <probe_IP> with the IP address of the probe system where the HTTP IoT Push Data Advanced sensor runs.
- Replace <token> with the Identification Token that you defined in the sensor settings.
- Change the Content type to application/json
- Add the following JSON to the Body field
{
"prtg": {
"text": "OK",
"result": [
{
"channel": "Latitude",
"float": 1,
"value": {lat}
},
{
"channel": "Longitude",
"float": 1,
"value": {lng}
},
{
"channel": "Accuracy",
"value": {radius}
}
]
}
}9. Click Ok to save the callback.
Device settings in PRTG
- Copy the ID of the HTTP IoT Push Data Advanced sensor. In this example, it is 2557.
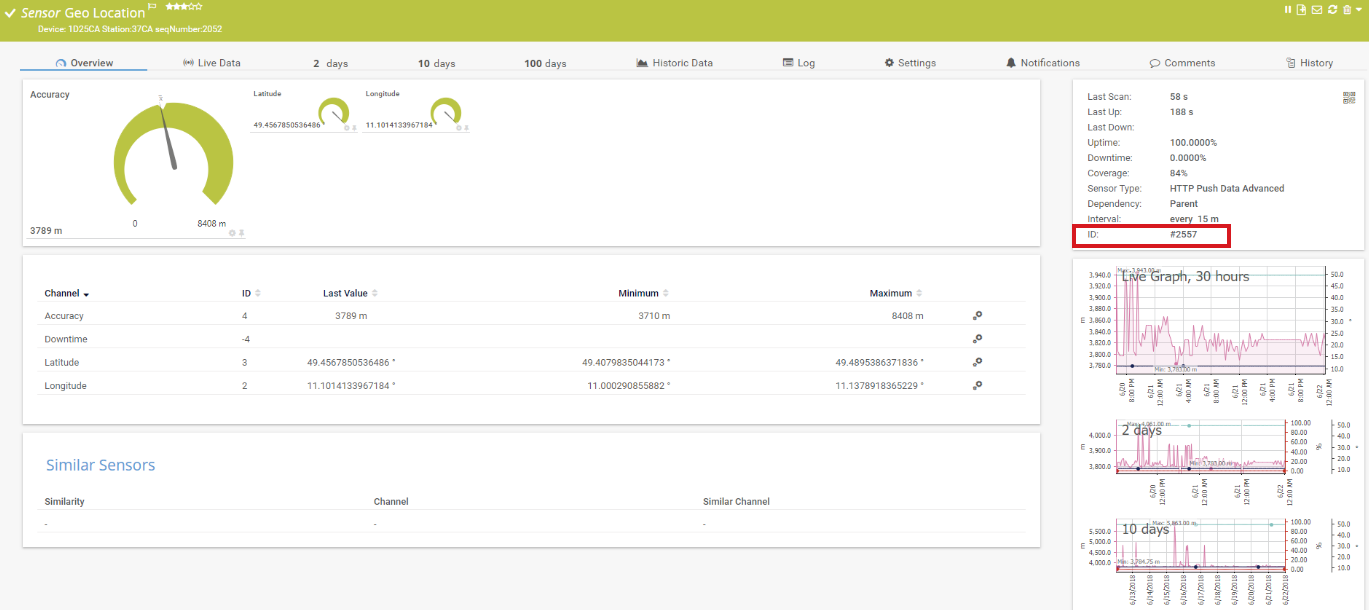
- In section Location of the settings of the device to which you added the sensor, disable the inheritance of settings.
- Enter the following under Location (for Geo Maps):
SigfoxTest{"id":<sensorid>,"count":1,"waypointstyle":null,"waypointmarker":2,"style":{"strokeColor":"#0404B4","strokeOpacity":0.0,"strokeWidth":4,"fillColor":"#0000ff","fillOpacity":0.1}} - Replace <sensorid> with the sensor's ID, which is 2557 in this example.
- Save your settings.
The geographical map now shows the Sigfox Geolocation, including the expected radius in which the device is located. 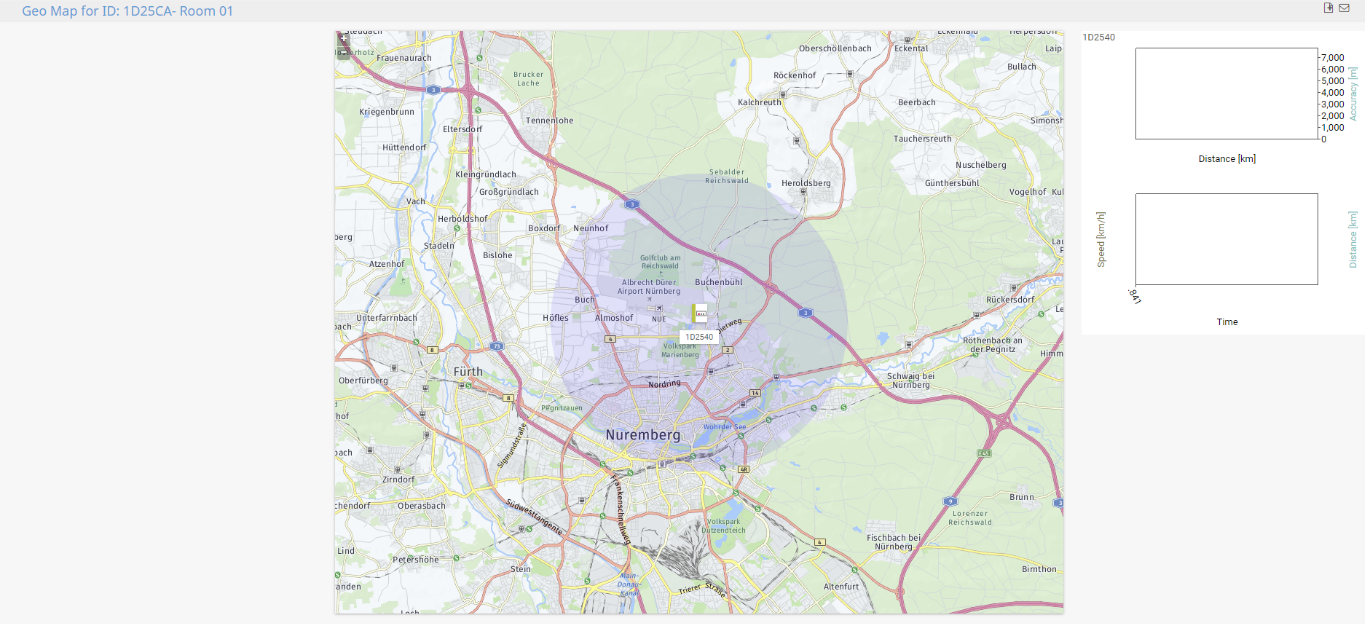
More
Disclaimer:
The information in the Paessler Knowledge Base comes without warranty of any kind. Use at your own risk. Before applying any instructions please exercise proper system administrator housekeeping. You must make sure that a proper backup of all your data is available.
